
Temperature
rise in a motor is the difference in temperature between the motor and its
environment, caused by the heat generated during its operation. Within the
motor, there are components like the iron core and the skeleton. Iron losses
occur due to the initial alternating magnetic field in the iron core during
operation. When the skeleton is energized, it experiences copper losses.
Additionally, there are stray losses, which manifest as heat. These factors
collectively contribute to the motor's temperature increase, affecting its
efficiency.
The insulation level of a motor pertains to the heat resistance of the insulation materials used, typically categorized into A, E, B, F, H, and C levels. The allowable temperature rise refers to how much the motor's temperature can increase relative to the ambient temperature. Insulating materials are crucial components, especially those that must withstand high temperatures. Different insulating materials exhibit varying heat resistance properties, impacting the motor's performance.
Insulation
temperature class A E B F H C
Maximum
allowable temperature (℃) 105 120 130 155 180 220
Skeleton
temperature rise limit (K) 60 75 80 100 125 150
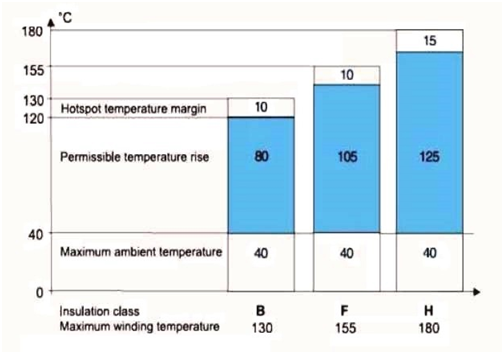
Generally, stepper motors are equipped with Class B insulation, which means the internal temperature should not exceed 130 degrees Celsius. Considering that the normal temperature is within 40 degrees, the surface temperature is kept below 90 degrees. (Therefore, for most stepper motors, a surface temperature of 60 degrees is considered normal.)
In high-temperature environments, it's advisable to use high-temperature-resistant stepper motors, such as Class H. When selecting materials like enameled wire, skeleton, magnets, bearings, grease, and end caps, it's essential to ensure they can withstand the maximum temperature required.
>> Enameled wire plays a critical role in high-temperature environments, as its heat resistance directly impacts safety. Ordinary-grade enameled wire softens or melts under high temperatures, potentially damaging the motor.
>> Magnets are another essential component, and their heat resistance indirectly affects motor performance. As temperature rises, a magnet's magnetic force weakens, leading to reduced torque. Selecting high-temperature-resistant magnets can prevent demagnetization, ensuring stable torque output.
>> The wire frame, used to wind coils and support the motor stator, is typically made of plastic. Using high-temperature-resistant materials for the wire frame is crucial to prevent deformation and extend its service life.

If you have more requirements for the stepper motors' temperature, please contact us for customization.